Both preventive maintenance and predictive maintenance are strategies aimed at reducing asset failure and increasing equipment reliability. Each offers unique benefits and organizations can choose to implement either strategy depending on a range of factors, such as asset criticality, organization size, cost, and effectiveness.
What is preventive maintenance
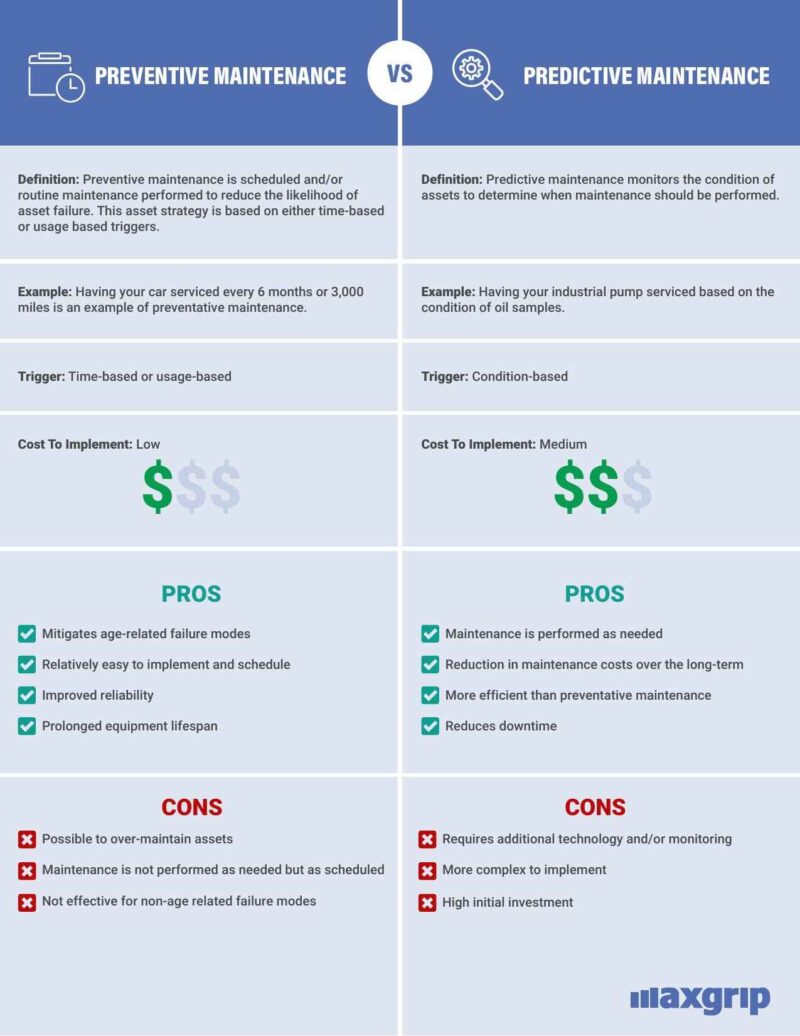
A preventive maintenance program is scheduled or routine maintenance that is performed to reduce the likelihood of asset failure. Everything from adjustments and cleaning to lubrication and part replacements can be a form of preventative maintenance. Preventive maintenance tasks are scheduled based either on a time-based or usage-based trigger.
Time-based preventive maintenance
This form of routine maintenance is based on planned time intervals and is performed regardless of asset condition. Assets vary, and the maintenance intervals for different assets will vary. The goal is to identify the maximum time interval that a piece of equipment will operate successfully and then schedule the routine maintenance accordingly. This approach is reliant on the assumption that the asset’s failure can at least in part be predicted by time. Having your car serviced every six months is an example of time-based preventive maintenance.
Usage-based preventive maintenance
This approach is based on usage triggers instead of fixed time intervals. Examples of usage-based maintenance include actions after a certain amount of cycles, miles, or hours of operation. These triggers are based on meter readings. Continuing the example of a car, having it serviced every 3,000 miles is usage-based maintenance.
What is predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance monitors the condition of assets to determine maintenance needs. Contrasting preventive maintenance, predictive maintenance monitors equipment in real-time for troubling indications. This approach proactively identifies potential failures to get ahead of the problem before it occurs.
A predictive maintenance approach would consist of having an industrial pump serviced based on the condition of oil samples. Because predictive maintenance requires condition monitoring in real-time, a drawback to this approach is the required technology and/or software. While this adds initial costs upfront, a predictive approach avoids the issue of over-maintenance that can occur with preventive maintenance.
Get inspired
Join Justin Satink in our "Asset Performance" webinar. Uncover MaxGrip's global assessment insights, benchmark results, and a real-world case study. 26th September, 9 am CT | 4 pm CEST. Don't miss it!
Discover MaxGrip's standout role in Industrial Asset Management Technology with our Verdantix-backed report. Unveil the insights that position MaxGrip as the only innovator in this field. Download now your copy.
An article about the differences between RCM and RCA. We discuss the benefits and share advice on the maintenance approaches.




